Azure Synapse Writer
Writes to Azure Synapse (formerly Azure SQL Data Warehouse).
Prerequisites:
Deploy an Azure Synapse instance.
Deploy an Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage instance to be used for staging the data. See Best practices for loading data into a dedicated SQL pool in Azure Synapse Analytics.
Optionally, connect the Azure Synapse instance and the Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 instance with an Azure Virtual Network (VNet). See Impact of using VNet Service Endpoints with Azure storage, particularly the prerequisites and the instructions for creating a database master key.
Create an Azure Synapse user for use by Striim. The user must have either the db_owner role or the db_datareader, db_datawriter, db_ddladmin, and bulkadmin permissions.
Create an Azure Synapse database scoped credential with the storage account name as the IDENTITY and the storage account access key as the SECRET. For example:
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD='<password>'; CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL AppCred WITH IDENTITY = '<storage account name>', SECRET = '<access key>';
You can view scoped credentials with the command:
SELECT * FROM sys.database_scoped_credentials;
If using MERGE mode:
If Merge API is AZURE_MERGE, Synapse requres all target tables to be hash-distributed. See Guidance for designing distributed tables using dedicated SQL pool in Azure Synapse Analytics.
For best performance, partition the tables (see Partitioning tables in dedicated SQL pool). If an Oracle source column is used as the partition column, the source column must have supplemental logging enabled.
Source tables must not have more than approximately 510 columns if Optimized Merge is False and not more than approximately 340 columns if Optimized Merge is True. This is due to Synapse's limit of 1024 columns per join in staging (see Capacity limits for dedicated SQL pool in Azure Synapse Analytics; Striim requires multiple columns in staging for each column in the source.
Azure Synapse Writer properties
property | type | default value | notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Account Access Key | String | the account access key for the storage account from Storage accounts > <account name> > Access keys | |
Account Name | String | the storage account name | |
CDDL Action | String | Process | See Handling schema evolution. If TRUNCATE commands may be entered in the source and you do not want to delete events in the target, precede the writer with a CQ with the select statement When Optimized Merge is True, CREATE statements will cause the application to halt. |
Client Configuration | String | If using a proxy, specify | |
Column Delimiter | String | | | If the data to be written may contain the default column delimiter (ASCII / UTF-8 124), specify a different delimiter that will never appear in the data. |
Connection Profile Name | String | Appears in Flow Designer only when Use Connection Profile is True. See Introducing connection profiles. | |
Connection Retry Policy | String | initialRetryDelay=10s, retryDelayMultiplier=2, maxRetryDelay=1m, maxAttempts=10, totalTimeout=10m | With the default setting, if a connection attempt is unsuccessful, the adapter will try again in 10 seconds ( The adapter will halt when either
If To disable connection retry, set Negative values are not supported. |
Connection URL | String | the JDBC connection URL for Azure Synapse, in the format Alternatively, you may use Active Directory authentication (see Supporting Active Directory authentication for Azure). | |
Excluded Tables | String | If | |
Ignorable Exception Code | String | Set to TABLE_NOT_FOUND to prevent the application from terminating when Striim tries to write to a table that does not exist in the target. See Handling "table not found" errors for more information. Ignored exceptions will be written to the application's exception store (see CREATE EXCEPTIONSTORE). | |
Merge API | String | STRIIM_MERGE |
|
Mode | String | MERGE | With the default value of MERGE, inserts and deletes in the source are handled as inserts and deletes in the target (as detailed in the notes for Merge API). Set to APPENDONLY to handle all operations as inserts. With this setting:
|
Optimized Merge | Boolan | False | Not supported when Merge API is STRIIM_MERGE. Set to True only when Mode is MERGE and the target's input stream is the output of an HP NonStop reader, or Oracle Reader source and the source events will include partial records. For HP NonStop, “partial records” means Set to True also when the source is Oracle Reader and the source table includes BLOB or CLOB columns When Optimized Merge is True, CDDL CREATE statements will cause the application to halt. |
Parallel Threads | Integer | See Creating multiple writer instances (parallel threads). Not supported when Mode is MERGE. | |
Password | encrypted password | The password for the specified user. See Encrypted passwords. | |
Storage Access Driver Type | String | WASBS | Set to ABFS if you are using an Azure Data Lake Storage instance for staging the data, or if you are using a general-purpose blob storage instance connected to Synapse using VNet or across a firewall. (See The Azure Blob Filesystem driver (ABFS) for more information.) Leave at the default setting WASBS if using a general-purpose V1 or V2 blob storage account without VNet or a firewall. |
Tables | String | Specify the name(s) of the table(s) to write to, in the format If the source is Database Reader and its Create Schema property is True, the specified schema(s) and table(s) will be created in the target (see the discussion of Create Schema in Database Reader properties for more details). Otherwise, the table(s) must exist in the target when the application is started, and if a specified target table does not exist, the application will terminate with an error. To skip writes to missing tables without terminating, specify TABLE_NOT_FOUND as an Ignorable Exception Code. When the target's input stream is a user-defined event, specify a single table. If the source table has no primary key, you may use the When the input stream of the target is the output of a DatabaseReader, IncrementalBatchReader, or SQL CDC source (that is, when replicating data from one database to another), it can write to multiple tables. In this case, specify the names of both the source and target tables. You may use the source.emp,target.emp source.db1,target.db1;source.db2,target.db2 source.%,target.% source.mydatabase.emp%,target.mydb.% source1.%,target1.%;source2.%,target2.% MySQL and Oracle names are case-sensitive, SQL Server names are not. Specify names as See Mapping columns for additional options. | |
Upload Policy | String | eventcount:10000, interval:5m | The upload policy may include eventcount and/or interval (see Setting output names and rollover / upload policies for syntax). Cached data is written to the storage account every time any of the specified values is exceeded. With the default value, data will be written every five minutes or sooner if the cache contains 10,000 events. When the app is undeployed, all remaining data is written to the storage account. |
Use Connection Profile | Boolean | False | |
Username | String | the user name Striim will use to log in to the Azure Synapse specified in ConnectionURL |
Azure Synapse Writer sample application
The following sample application would read from Oracle using IncrementalBatchReader and write to Azure Synapse.
CREATE SOURCE ibr2azdw_Source USING IncrementalBatchReader ( Username: 'striim', Password: '********', ConnectionURL: '192.0.2.1:1521:orcl', Tables: 'MYSCHEMA.TABLE1', CheckColumn: 'MYSCHEMA.TABLE1=UUID', StartPosition: 'MYSCHEMA.TABLE1=1234' ) OUTPUT TO ibr2azdw_Source_Stream ; CREATE TARGET ibr2azdw_AzureSynapseTarget1 USING AzureSQLDWHWriter ( Username: 'striim', Password: '********', ConnectionURL: 'jdbc:sqlserver://testserver.database.windows.net:1433;database=rlsdwdb', Tables: 'MYSCHEMA.TABLE1,dbo.TABLE1', AccountName: 'mystorageaccount' AccountAccessKey: '********' ) INPUT FROM ibr2azdw_Source_Stream;
Azure Synapse data type support and correspondence
TQL type | Azure Synapse type |
|---|---|
java.lang.Byte | tinyint |
java.lang.Double | float |
java.lang.Float | float |
java.lang.Integer | int |
java.lang.Long | bigint |
java.lang.Short | smallint |
java.lang.String | char, nchar, nvarchar, varchar |
org.joda.time.DateTime | datetime, datetime2, datetimeoffset |
When the input of an Azure Synapse target is the output of a MySQL source (DatabaseReader, IncremenatlBatchReader, or MySQLReader):
MySQL type | Azure Synapse type |
|---|---|
bigint | bigint, numeric |
bigint unsigned | bigint |
binary | binary |
char | nchar |
date | date |
datetime | datetime, datetime2, datetimeoffset |
decimal | decimal |
decimal unsigned | decimal |
double | money, smallmoney |
float | float, real |
int | int |
int unsigned | int |
longblob | varbinary |
longtext | varchar |
mediumblob | binary |
mediumint | int |
mediumint unsigned | int |
mediumtext | varchar |
numeric unsigned | int |
smallint | smallint |
smallint unsigned | smallint |
text | varchar |
time | time |
tinyblob | binary |
tinyint | bit (if only one digit), tinyint |
tinyint unsigned | tinyint |
tinytext | varchar |
varbinary | varbinary |
varchar | nvarchar, varchar |
year | varchar |
When the input of an Azure Synapse target is the output of an Oracle source (DatabaseReader, IncremenatlBatchReader, or OracleReader):
Oracle type | Azure SQL Data Synapse type |
|---|---|
binary_double | float |
binary_float | real |
blob | binary, varbinary |
char | char |
clob | nvarchar |
date | date |
float | float |
nchar | nchar |
nclob | varchar |
number(1) | bit |
number(10,4) | smallmoney |
number(10) | int |
number(19,4) | money |
number(19) | bigint |
number(3) | tinyint |
number(5) | char, smallint |
timestamp | datetime, datetime2, datetimeoffset |
timestamp with local timezone | datetimeoffset |
timestamp with timezone | datetimeoffset |
varchar2 | varchar |
varchar2(30) | time |
xmltype | varchar |
When the input of an AzureSynapse target is the output of a SQL Server source (DatabaseReader, IncremenatlBatchReader, or MSSQLReader):
SQL Server type | Azure Synapse type |
|---|---|
bigint | bigint |
binary | binary |
bit | bit, char |
date | date |
datetime | datetime |
datetime2 | datetime2 |
datetimeoffset | datetimeoffset |
decimal | decimal |
float | float |
image | varbinary |
int | int |
money | money |
nchar | nchar |
ntext | varchar |
numeric | numeric |
nvarchar | nvarchar |
nvarchar | nvarchar |
real | real |
smalldatetime | smalldatetime |
smallint | smallint |
smallmoney | smallmoney |
text | varchar |
time | time |
tinyint | tinyint |
varbinary | varbinary |
varchar | varchar |
xml | varchar |
Using manual OAuth with Azure Synapse Writer
For simpler OAuth setup, create an Azure Synapse connection profile that uses the Entra ID or Entra Service Principal authentication type.
Register and configure an application
Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform as described in Learn / Microsoft Entra / Microsoft identity platform / Quickstart: Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform.
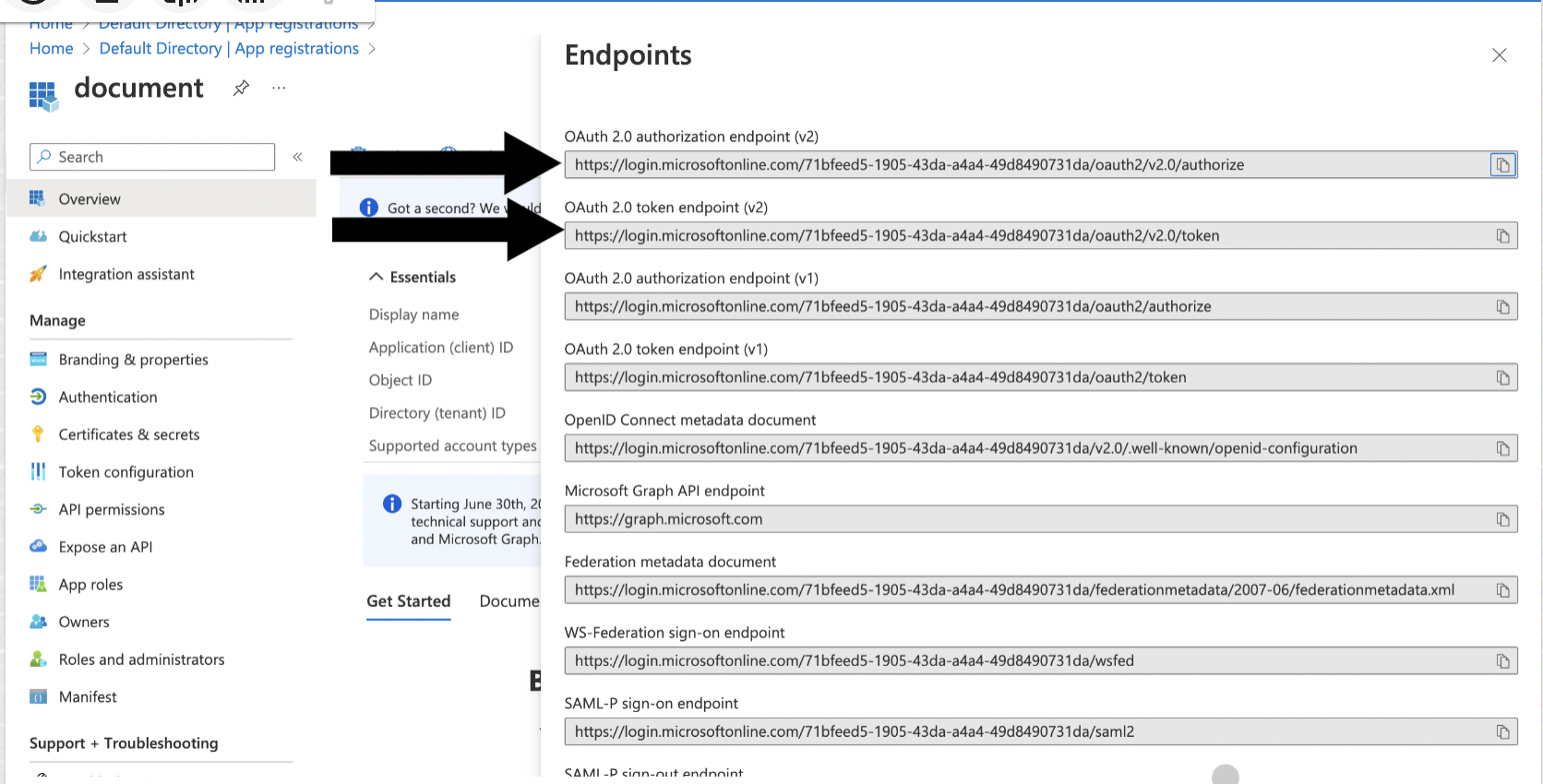
Note the Client (application) ID, Tenant (directory) ID, Client Secret, Authorize Endpoint, and Token Endpoint, you will need them when creating the connection profile.
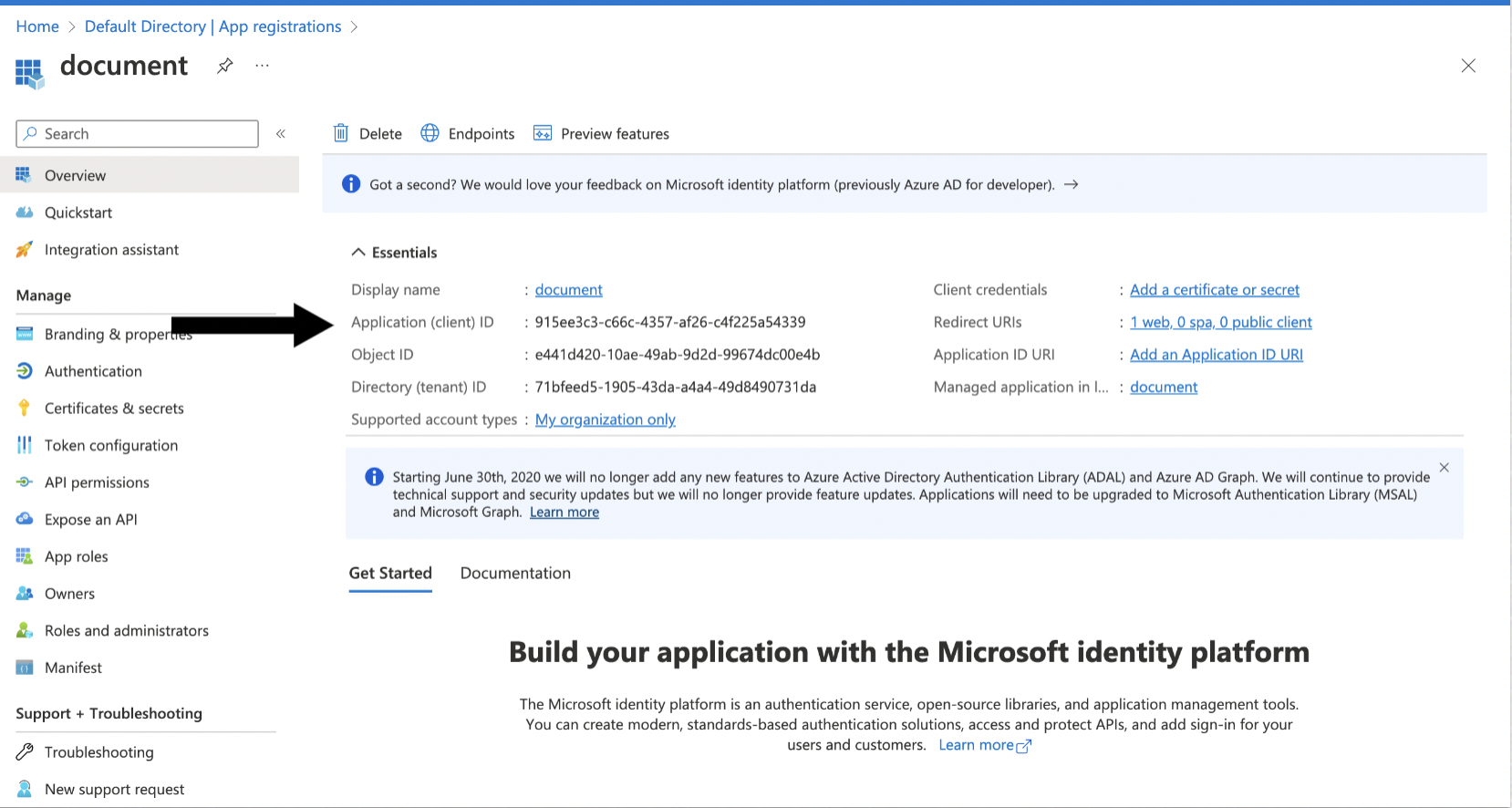
Go to Certificates and Secret and click New Client Secret. Note the value of the secret, you will need it when creating the connection profile.
Go to the registered app, select API permissions, and add the Azure SQL Database (user_impersonation) permission.
Generate the refresh token using a web browser and curl
Call lthe authorization endpoint by pasting the following into your browser's address bar, replacing
<tenant ID>and<client ID>with the values from "Register and configure an application" and<state>with a random number or some encoded information. To validate the integrity of information exchange, verify that this state value matches the one that in the response payload later in this procedure.https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant ID>/oauth2/v2.0/authorize?client_id=<client ID> &response_type=code &redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost &response_mode=query &scope=https%3A%2F%2Fdatabase.windows.net%2F.default%20offline_access &state=<state>
When prompted, log in as a user with access to the Azure Synapse data warehouse. The browser will return a URL containing an authorization code (the portion between
code=and&state).http://localhost/?code= 0.ARsA1e6_cQUZ2kOkpEnYSQcx2uiQ8dwVo7tCoLGGBj_xw0AbAAA.AgABAAIAAAD--DLA3VO7QrddgJg7WevrAgDs _wUA9P_wji3IyHTg8MQUOqXFtdwUIwVEnR4oCGj0P_l3JfxA3XNfyKczWKpfI87VOu2xrgPodU6y3cs7uyFsy66iia FVMyUd9tIQijRur2mn6lI3OSJHKBHWaVs0Ii8FKQmWJxHRaxUctfJ_Fd9b_ZwmLSSK0pDqTEykK79I_jUXTCsChqq2 R30ztAPHmbwTcu4tTbTLLCuX1O1Kho2wq4KsMl3DQTPciHjXcNJ8Qz0rE909Hn7-wxliNstT3xbYj8V7g1aC3_3N_h jZk7RK6VBmgoStBXcMzckGB0ec34g1p4j7YCh5qAhyNX7lePy1m0IOX88XghY2mFlN_UiotZIwCkA2ZNzTEpxnFhOy L6JilQSGLOoQtP1VGL91ZmB6okhsEZbI8IvJqLvnpwz0N3HMpPJ3jQTQXCVGnla7vQAWyKHBuhRNEA84q8s37E6N-u N3BV16ym_zQWmIAcdgTPMIlbrKbnbpjbv6sbg3uMSs3Chq9mDawxJrh_atw &state=12345&session_state=bf8f7e74-bc50-47a9-a1ee-0db219cb06b0#
Using curl, execute the following command, replacing <client ID> and <client secret> with the values from "Register and configure an application" and
<authorization code>with the string from the previous step. Note the value of the returned refresh token, you will need it when creating the connection profile..curl -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \ https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant-id>/oauth2/v2.0/token \ -d 'client_id=<client ID>' \ -d 'client_secret=<client secret>' \ -d 'scope=https%3A%2F%2Fdatabase.windows.net%2F.default%20offline_access' \ -d 'code=<authorization code>' \ -d 'redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost' \ -d 'grant_type=authorization_code' \ -d 'state=12345'
Create a connection profile
Create an Azure Synapse connection profile (see Introducing connection profiles).